The Evil Eye in Islam
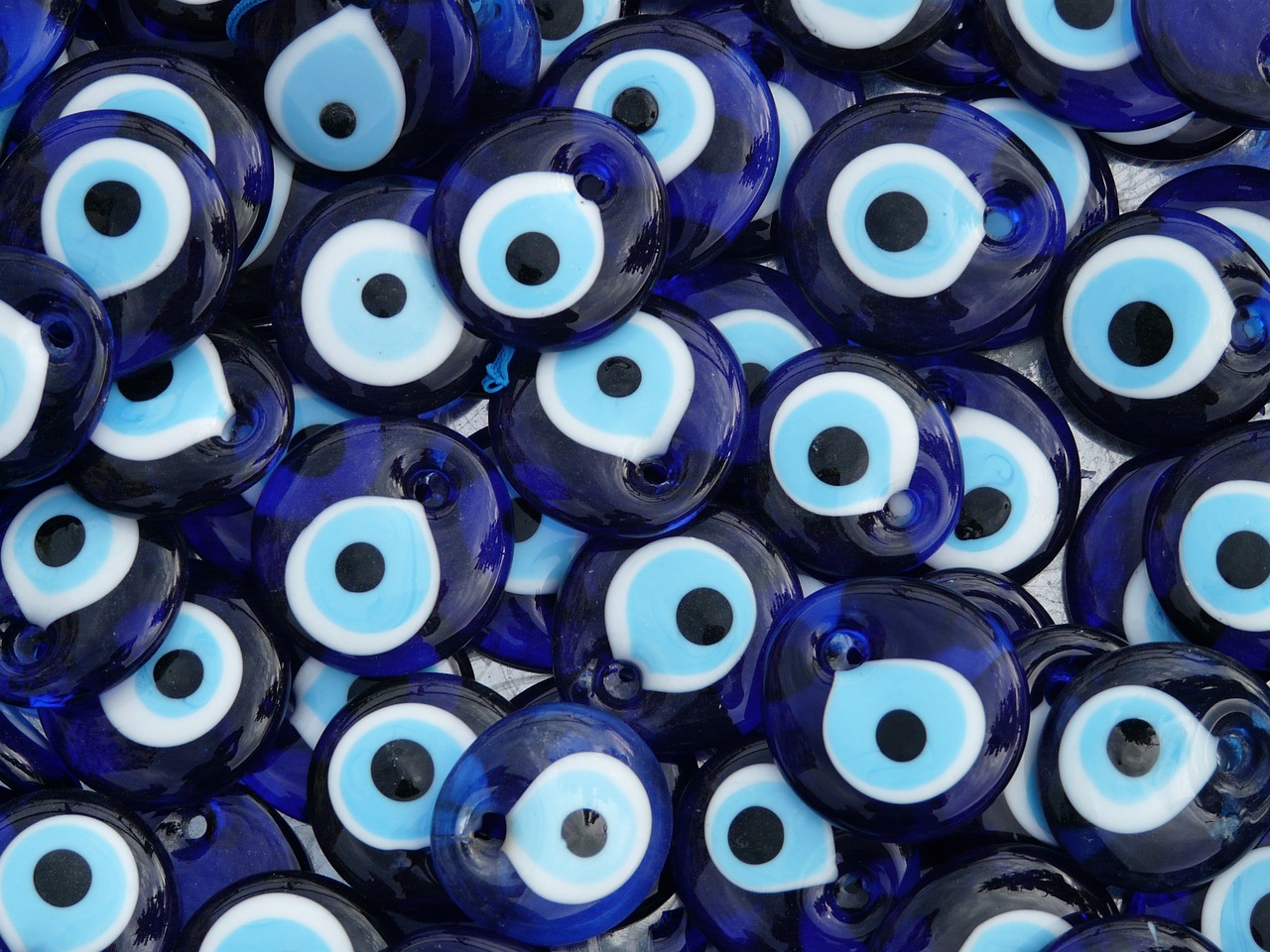

The Evil Eye in Islam: Unraveling Beliefs, Traditions, and Protection Introduction The concept of the ‘evil eye’ transcends cultures and histories, yet in the realm of Islamic tradition, it holds a distinct significance. This belief, embedded in both religious scriptures and cultural practices, is not just a superstition but a deeply rooted part of Islamic […]
What Does Islam Mean?

Understanding the Essence of Islam: What Does Islam Mean? Introduction The term ‘Islam’ is commonly recognized worldwide, given that it represents one of the largest religions. However, a deep dive into its semantics and spiritual underpinnings reveals profound layers. In this post, we will journey through the linguistic roots, historical backdrop, and spiritual ethos that […]
What is Islam? – A Comprehensive Guide

What is Islam? – A Comprehensive Guide Introduction Islam, with over a billion followers, is among the world’s major religions. It stands not merely as a system of beliefs but as a holistic way of life. This post delves into the richness of its beliefs, history, and practices. Historical Foundations Origins: Islam’s genesis traces back […]
Top Kids’ Courses: Boosting Knowledge & Fostering Lifelong Learning

Top Kids’ Courses: Boosting Knowledge & Fostering Lifelong Learning Empowering Children’s Future: The Significance of Learning the Arabic Language Children, the blossoming buds of our community, are inherent learners with an insatiable curiosity. In this dynamic era where globalization and intercultural interactions are prevalent, equipping our children with an additional language is akin to handing […]